If you want to make your hands dirty with the code, you can follow the instructions below to install and run the YServer and YClient applications.
Mind that if you are interested to use the web interface to interact with the platform, just follow the instructions in the Y Social page.
The following guide is intended for users who want to run the YServer and YClient applications locally and interact with the platform using the command line.
🔴 Note: Some information might not be up to date or missing due to the ongoing development of the project.
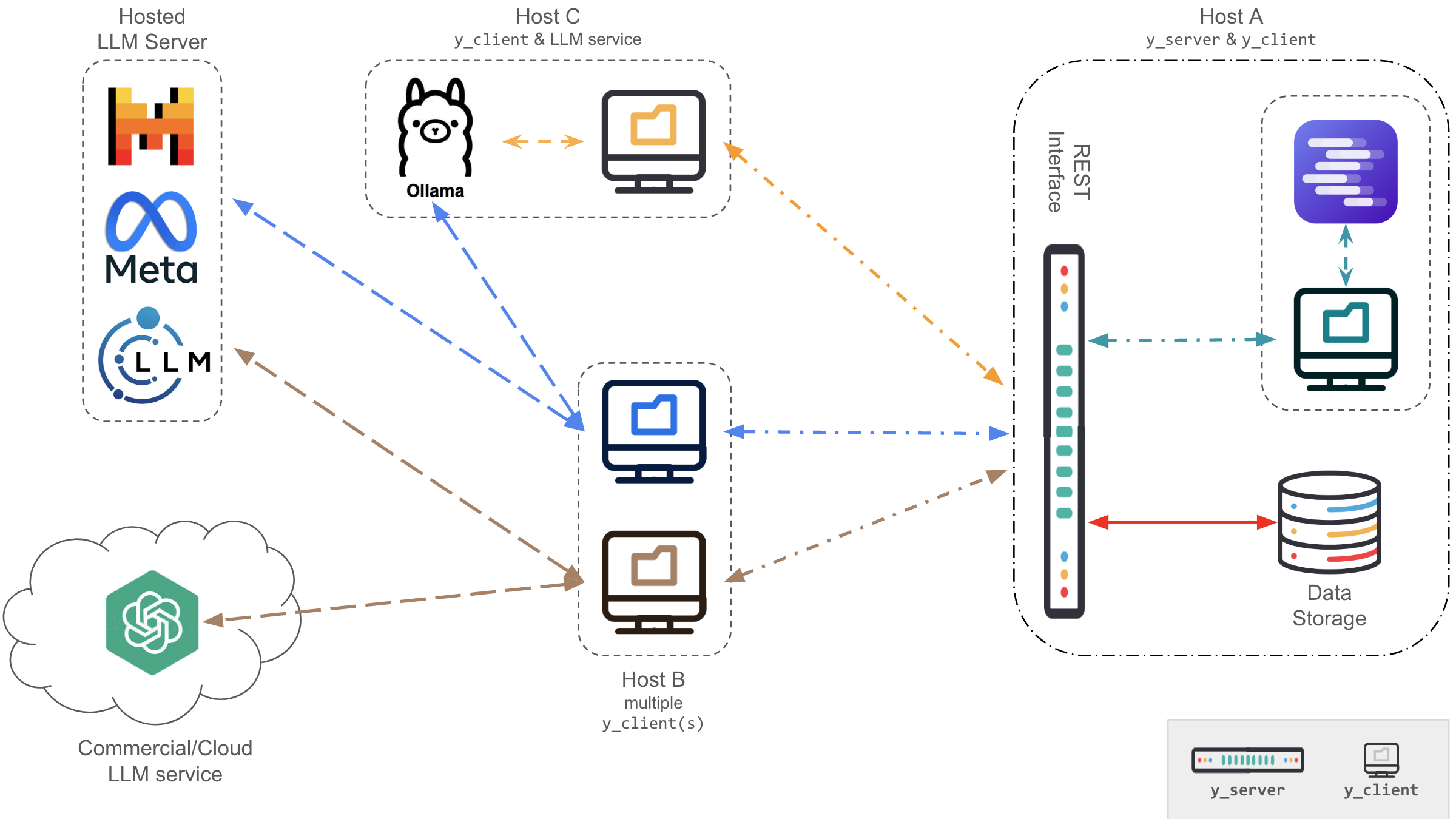
Y Server
Y Server is a server-side application that exposes a set of REST APIs that simulate the actions of a microblogging social platform.
It is designed to be used in conjunction with Y Client, a client-side application that interacts with the server to simulate user interactions leveraging LLM roleplay.
Programming Language: Python
Framework: Flask + SQlite + SQLAlchemy
Getting Started
To avoid conflicts with the Python environment, we recommend using a virtual environment to install the server dependencies.
Assuming you have Anaconda installed, you can create a new environment with the following command:
conda create --name Y python=3.11
conda activate Y
Clone the repository to your local machine
git clone https://github.com/YSocialTwin/YServer.git
Once obtained the Y Server (and decompressed it whenever needed), open a terminal, move to its main directory and install its dependencies using
cd YServer
pip install requirements_server.txt
Run the server
Set the server preferences modifying the file config_files/exp_config.json:
{
"name": "local_test",
"host": "0.0.0.0",
"port": 5010,
"debug": "True",
"reset_db": "False",
"modules": ["news", "voting", "image"]
}
where:
nameis the name of the experiment (will be used to name the simulation database - which will be created under the folderexperiments);hostis the IP address of the server;portis the port of the server;reset_dbis a flag to reset the database at each server start;debugis a flag to enable the debug mode;modulesis a list of additional modules to be loaded by the server (e.g., news, voting). Please note that the YClient must be configured to use the same modules.
Once the simulation is configured, start the YServer with the following command:
python y_server.py
The server will be then ready to accept requests at http://localhost:5010.
Available Modules
- News: This module allows the server to access online news sources leveraging RSS feeds.
- Voting: This module allows the agents to cast their voting intention after interacting with peers contents (designed to perform political debate simulation).
- Image: This module allows agents to share images (obtained from the headlines of RSS feed items - thus it requires the News module to be active) and comment on them.
Y Client
Y Client is a client-side application that interacts with the server to simulate user interactions leveraging LLM roleplay.
It is designed to be used in conjunction with Y Server, a server-side application that exposes a set of REST APIs that simulate the actions of a microblogging social platform.
Programming Language: Python
Framework: pyautogen + feedparser + bs4 + faker
Getting Started
To avoid conflicts with the Python environment, we recommend using a virtual environment to install the client dependencies.
Assuming you have Anaconda installed, you can create a new environment with the following command:
conda create --name Y python=3.11
conda activate Y
Clone the repository to your local machine
git clone https://github.com/YSocialTwin/YClient.git
Once obtained the Y Client (and decompressed it whenever needed), open a terminal, move to its main directory and install its dependencies using
cd YClient
pip install requirement_client.txt
Run the client
Remember to start the YServer before running the client and verify that the LLM server is running and accessible.
The REST API exposed by the server can be used to implement several variants of the client.
y_client.py exposes a simple commandline client that can be instantiated using the following command:
python y_client.py [flags] [arguments]
Several parameters can be specified while launching y_client.py:
Use the flags and their respective arguments as described below:
| Parameter | Flag | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Configuration File | -c | config.json | JSON file describing the simulation configuration. |
| Agents | -a | None | JSON file with pre-existing agents (needed to resume an existing simulation). |
| Feeds | -f | rss_feeds.json | JSON file containing RSS feed categorized. |
| Owner | -o | admin | Simulation owner username (useful in multi-client scenarios). |
| Reset | -r | False | Boolean. Whether to reset the experiment status. If set to True, the simulation will start from scratch (the DBs will be cleared). |
| News | -n | False | Boolean. Whether to reload the RSS feeds. If set to True, the RSS feeds will be reloaded (the RSS-client DB will be cleared). |
| Initial Social Graph | -g | None | Name of the graph file (CSV format, number of nodes equal to the starting agents - ids as consecutive integers starting from 0) to be used for the simulation. |
| Content Recommender System | -x | ReverseChronoFollowersPopularity | Name of the content recommender system to be used. Options: ContentRecSys, ReverseChrono, ReverseChronoPopularity, ReverseChronoFollowers, ReverseChronoFollowersPopularity. |
| Follower Recommender System | -y | PreferentialAttachment | Name of the follower recommender system to be used. Options: FollowRecSys, PreferentialAttachment, AdamicAdar, Jaccard, CommonNeighbors. |
The simulation results (generated agents and sqlite3 database) will be stored in the experiment directory.
Examples
To start a fresh simulation with a specific scenario configuration (as described by the config.json and rss_feed.json files), use the following command:
python y_client.py -c config.json -f rss_feeds.json -o your_name -r True -n True -x ReverseChronoFollowersPopularity -y PreferentialAttachment
To resume an existing simulation, use the following command:
python y_client.py -a agents.json -o your_name
In this latter case, the agents.json file will be used to log the agents on the YServer and resume the simulation from the last available server simulation round.
Remember to modify the config.json file to specify the LLM server address, port and model to be used. For more information, see the scenario configuration documentation.
NB: YServer allows to transparently execute multi-client simulations. In this case, the owner parameter is used to distinguish the agents generated by different clients.
YClient Simulation Loop
The following is a simplified and non-comprehensive pseudocode-version of the simulation loop implemented by y_client/clients/client_base.py:
# Input: config: Simulation configuration Files
# Input: feeds: RSS feeds
# configuring agents and servers
agents = create_agents(config)
pages = create_pages(config, feeds) # see scenario documentation
agents = agents + pages
y_server = connect(config.servers.api)
for day in range(config.simulation.days):
for slot in range(config.simulation.slots):
#synchronize with the y_server clock
h = y_server.get_current_slot()
# identify the active agents for the current slot
expected_active = int(len(agents) * config.simulation.hourly_activity[h])
active = random.sample(agents, expected_active)
# available actions
acts = [a for a, v in config.simulation.actions_likelihood.items() if v > 0]
for agent in active:
for _ in round_actions:
# evaluate agent’s actions (once per activity slot)
agent.select_action(acts)
# reply to received mentions
agent.reply_mentions()
# evaluate following (once per day)
evaluate_following(active)
# increase the agent population
agents.add_new_agents()
# evaluate churn
agents.churn()
More complicated behaviors (allowing for more finegrained agents configurations) can be implemented by extending the y_client.clients.YClientBase class (see as an example y_client.clients.YClientWithPages).
Large Language Models (LLMs)
LLMs (Large Language Models) are a class of machine learning models that can generate human-like text. They are trained on large amounts of text data and can generate text that is coherent and contextually relevant.
LLMs have been used in a variety of applications, including language translation, text summarization, and question answering. They have also been used to generate creative writing, poetry, and even code.
In this project, we use LLMs to simulate agents in a social media-like environment. Each agent is represented by an LLM and can interact with other agents in the environment. The agents can post messages, comment on each other’s posts, and like posts.
Getting Started
YClient requires an OpenAI compatible LLM model to run. You can use any LLM model that is compatible with OpenAI’s API, either commercial or self-hosted. Here we will briefly describe how to set up a local LLMs server using ollama.
Step 1: Install ollama
First, you need to install ollama on your local machine. Download the latest release from the official website and follow the installation instructions.
Step 2: Configure the LLMs server
Once you have installed ollama, you need to pull the LLMs model you would like to use.
You can find a list of available models on the ollama models page.
To pull a model, use the following command:
ollama pull <model_name>
For example, to pull the llama3 model, you would run:
ollama pull llama3
Step 3: Start the LLMs server
To start the LLMs server, use the following command:
ollama start serve
This will start the LLMs server on your local machine. You can now use the server to interact with the LLMs model.
Step 4: Interact with the LLMs server
You can interact with the LLMs server using the ollama command-line tool.
ollama run llama3
This will start an interactive session with the llama3 model. You can type text and the model will generate a response.
Using ollama with YClient
To use ollama with YClient, you need to configure the client to connect to the LLMs server.
You can do this by editing the config.json (see Scenario Design) specifying as LLM server URL http://127.0.0.1:11434/v1 and as selected model llama3 (or any other model, or list of models, you have previously installed).
NB: Ollama is just one of the many options available to run LLMs locally. You can use any other LLMs server that is compatible with OpenAI’s API (e.g., LM Studio, llama-cpp-python).