Last time we spoke, we introduced our Zero-Code Platform, designed to make social simulations more accessible than ever before. However, we didn’t stop there.
As all first releases, the initial version was a little rough around the edges. Configuring simulations required some technical know-how, and the interface was still a work in progress.
Well, we’re excited to announce that we’ve listened to your feedback and made significant improvements!
🌟 What’s New?
With this update we are introducing several new features to enhance your simulation experience:
- Multi DBMS Support: Choose between SQLite and PostgreSQL for your simulation database.
- Revised Experiment workflow: A user-friendly process simulations configuration.
- More Realistic Agent Activity Patterns: Simulate more lifelike agent behaviors.
ySights: Advanced Data Analysis: A Python library to analyze and visualize simulation data.- Jupyter Lab Integration for Interactive Simulations: Seamlessly analyze your simulations with Experiments-specific Jupyter Notebooks embedded within the
YSocialAdmin panel.
Let’s dive into the details of these exciting new features!
🗄️ Multi-DBMS Support
You asked — we delivered.
YSocial now supports SQLite for lightweight experiments and PostgreSQL for large-scale studies.
# No additional configuration needed - SQLite is the default
python y_social.py
# Start YSocial with PostgreSQL (expecting a running PostgreSQL server)
python y_social.py --db postgresql
You can switch storage engines at startup, gaining better performance for large agent populations and improved cross-platform compatibility.
⚙️ Revised Experiment Workflow
Setting up simulations has never been easier.
We rebuilt the configuration UI to reduce complexity and increase clarity. Now, users benefit from:
- Simple experimental pipeline:
- Create population
- Create Experiment
- Create Simulation Client (linking population and experiment)
- Launch Experiment
- Clearer parameter grouping
- Restructured Agent Population setup
- Finegrained generated content annotation enabling/disabling (e.g., sentiment, toxicity, elicited emotions)




This means less time configuring, more time discovering insights.
🕒 Realistic Temporal Activity Patterns
Different users behave differently across time. YSocial now allows you to simulate heterogeneity in activity by defining:
- Global hourly activity distributions: what percentage of agents are active at each hour of the day
- Likelihoods of each agent to be selected to be active during each hour (differentiation between “highly active” and “less active” agents)
- Agents’ temporally consistent activity patterns (e.g., night owls vs. early birds)
- Etherogenous activity volumes when active (e.g., some agents perform more actions when active than others)
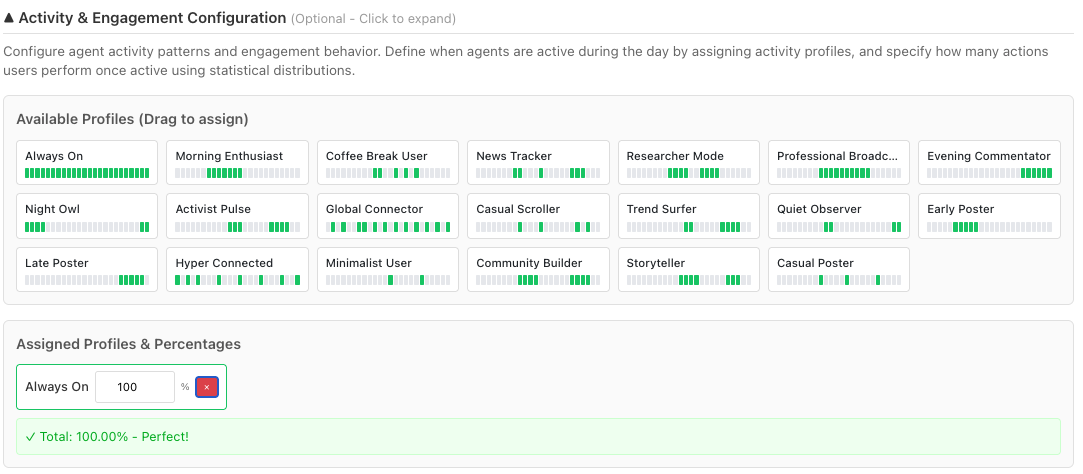
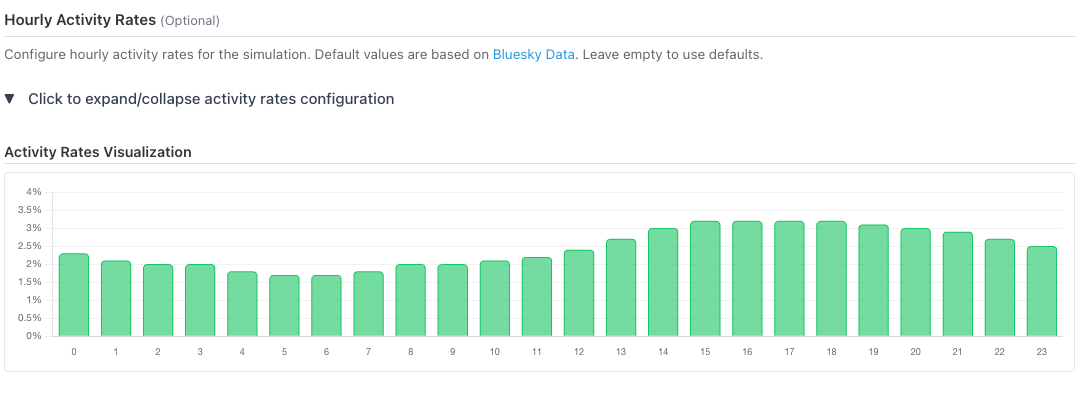

All these parameters make agent activity patterns more realistic, consistent and diverse. Moreover, they can be fitted on distributions extracted from real data – anyone said “Bluesky Social Dataset”?
🤖 OpenAI-Compatible LLM Server Integration
YSocial now supports multiple LLM services for content generation:
- Ollama (fast local inference)
- vLLM (high-throughput for large experiments)
- Any OpenAI-compatible server
# Use Ollama (default)
python y_social.py --llm-backend ollama
# Use vLLM
python y_social.py --llm-backend vllm
# remember to have vLLM server running with OpenAI compatible endpoints
# (instead of 'vllm serve' use 'python3 -m vllm.entrypoints.openai.api_server' to start the server)
# Use custom OpenAI-compatible server
python y_social.py --llm-backend myserver.com:8000
LLM-powered agents can generate persuasive text, evolve narratives, and produce multi-turn social interactions — fully configurable within the admin panel.
Remember: the LLM server is not tied to be running on the same machine as YSocial. Such flags are only needed if you want to host the LLM server on your local machine. If you have a remote server, you can provide its address within the Admin Panel and start YSocial with:
python y_social.py
📊 ySights — Your Analysis Companion
YSocial produces rich datasets — ySights makes them actionable.
📎 ySights GitHub
With ySights, you can analyze information cascades, influence pathways, narrative shifts, and measure moderation effects — all in Python, with ready-to-use visualization templates.

🧪 JupyterLab Integration
No more exporting databases or juggling tools. The Admin Panel now embeds Experiment-bounded JupyterLab, allowing you to:
- Run a simulation and immediately open an interactive notebook
- Load the experiment’s data with a single line of code
- Use
ySightsfor analysis, visualization, and hypothesis testing - Iterate rapidly without leaving the platform

Activate (or deactivate) JupyterLab directly from the Experiment configuration page. And if you don’t need it (or security constraints requires it), simply disable it on startup!
# No additional configuration needed - JupyterLab is enabled by default
python y_social.py
# Start YSocial with JupyterLab disabled
python y_social.py --no_notebook
🚀 What’s Next?
We’re actively working on:
- Forum-like platform simulations (Reddit/Voat like interface)
- Data ingestion from real social media platforms
- Pools integration: let agents vote on topics specific to their interests
- Goal-oriented agents with adaptive strategies
- Simulation-driven Opinion Dynamics annotation
- … and much more!
Your feedback guides our roadmap — keep it coming! 💬
🙌 Thank You for Believing in YSocial
This release reflects the growing community around YSocial — researchers, students, developers, and policy analysts — all working to understand and improve digital social systems.
We can’t wait to see what you create next. ✨
🔗 Resources
YSocial → GitHub
ySights → GitHub