Network Analysis with ySights
This tutorial demonstrates how to extract and analyze social networks from YSocial simulation data.
What You’ll Learn
Extracting different types of social networks
Computing network metrics
Analyzing ego networks
Visualizing network structures
[1]:
from ysights import YDataHandler
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Set up visualization
plt.style.use('seaborn-v0_8-whitegrid')
%matplotlib inline
[2]:
# Initialize data handler
db_path = 'ysocial_db.db'
ydh = YDataHandler(db_path)
1. Extracting the Social Network
The social network represents connections between agents (follows, friends, etc.).
[3]:
# Extract the full social network
social_network = ydh.social_network()
print("Social Network Statistics:")
print(f" Nodes (Agents): {social_network.number_of_nodes()}")
print(f" Edges (Connections): {social_network.number_of_edges()}")
print(f" Directed: {social_network.is_directed()}")
Social Network Statistics:
Nodes (Agents): 993
Edges (Connections): 29544
Directed: True
Network Density
Density measures how connected the network is (0 = no connections, 1 = fully connected).
[4]:
density = nx.density(social_network)
print(f"Network Density: {density:.4f}")
print(f" Interpretation: {density*100:.2f}% of all possible connections exist")
Network Density: 0.0300
Interpretation: 3.00% of all possible connections exist
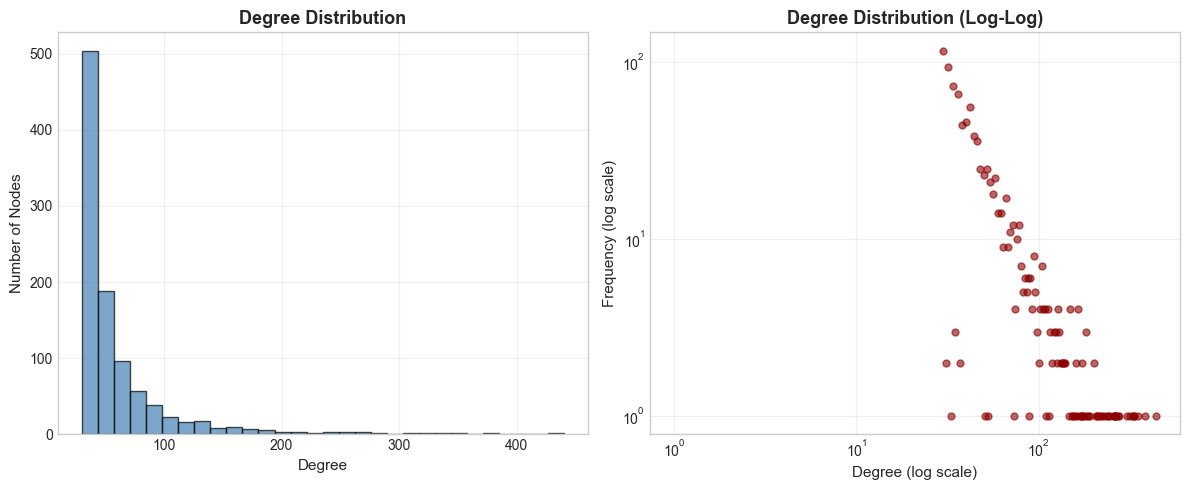
2. Degree Distribution Analysis
The degree of a node is the number of connections it has.
[5]:
# Calculate degree for all nodes
degrees = dict(social_network.degree())
degree_values = list(degrees.values())
print("Degree Statistics:")
print(f" Mean Degree: {np.mean(degree_values):.2f}")
print(f" Median Degree: {np.median(degree_values):.2f}")
print(f" Max Degree: {max(degree_values)}")
print(f" Min Degree: {min(degree_values)}")
Degree Statistics:
Mean Degree: 59.50
Median Degree: 42.00
Max Degree: 440
Min Degree: 30
[6]:
# Visualize degree distribution
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 5))
# Histogram
plt.subplot(1, 2, 1)
plt.hist(degree_values, bins=30, edgecolor='black', alpha=0.7, color='steelblue')
plt.xlabel('Degree', fontsize=11)
plt.ylabel('Number of Nodes', fontsize=11)
plt.title('Degree Distribution', fontsize=13, fontweight='bold')
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# Log-log plot
plt.subplot(1, 2, 2)
degree_counts = nx.degree_histogram(social_network)
degrees_range = range(len(degree_counts))
plt.loglog(degrees_range, degree_counts, 'o', markersize=5, alpha=0.6, color='darkred')
plt.xlabel('Degree (log scale)', fontsize=11)
plt.ylabel('Frequency (log scale)', fontsize=11)
plt.title('Degree Distribution (Log-Log)', fontsize=13, fontweight='bold')
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
3. Centrality Measures
Centrality measures identify the most important nodes in the network.
Degree Centrality
Identifies nodes with the most direct connections.
[7]:
# Calculate degree centrality
degree_centrality = nx.degree_centrality(social_network)
# Find top 5 most central nodes
top_5_degree = sorted(degree_centrality.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)[:5]
print("Top 5 Nodes by Degree Centrality:")
for i, (node, centrality) in enumerate(top_5_degree, 1):
print(f" {i}. Node {node}: {centrality:.4f}")
Top 5 Nodes by Degree Centrality:
1. Node 2: 0.4435
2. Node 25: 0.3851
3. Node 23: 0.3528
4. Node 18: 0.3367
5. Node 21: 0.3347
Betweenness Centrality
Identifies nodes that act as bridges between different parts of the network.
[8]:
# Calculate betweenness centrality (may take time for large networks)
# Use a sample if network is very large
if social_network.number_of_nodes() > 1000:
print("Large network detected. Computing approximate betweenness...")
betweenness = nx.betweenness_centrality(social_network, k=100) # Sample 100 nodes
else:
betweenness = nx.betweenness_centrality(social_network)
top_5_betweenness = sorted(betweenness.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)[:5]
print("Top 5 Nodes by Betweenness Centrality:")
for i, (node, centrality) in enumerate(top_5_betweenness, 1):
print(f" {i}. Node {node}: {centrality:.4f}")
Top 5 Nodes by Betweenness Centrality:
1. Node 2: 0.0405
2. Node 25: 0.0325
3. Node 23: 0.0279
4. Node 18: 0.0253
5. Node 28: 0.0235
4. Mention Network
The mention network shows who mentions whom in their posts.
[9]:
# Extract mention network
mention_network = ydh.mention_network()
print("Mention Network Statistics:")
print(f" Nodes: {mention_network.number_of_nodes()}")
print(f" Edges (Mentions): {mention_network.number_of_edges()}")
print(f" Density: {nx.density(mention_network):.4f}")
Mention Network Statistics:
Nodes: 956
Edges (Mentions): 11598
Density: 0.0127
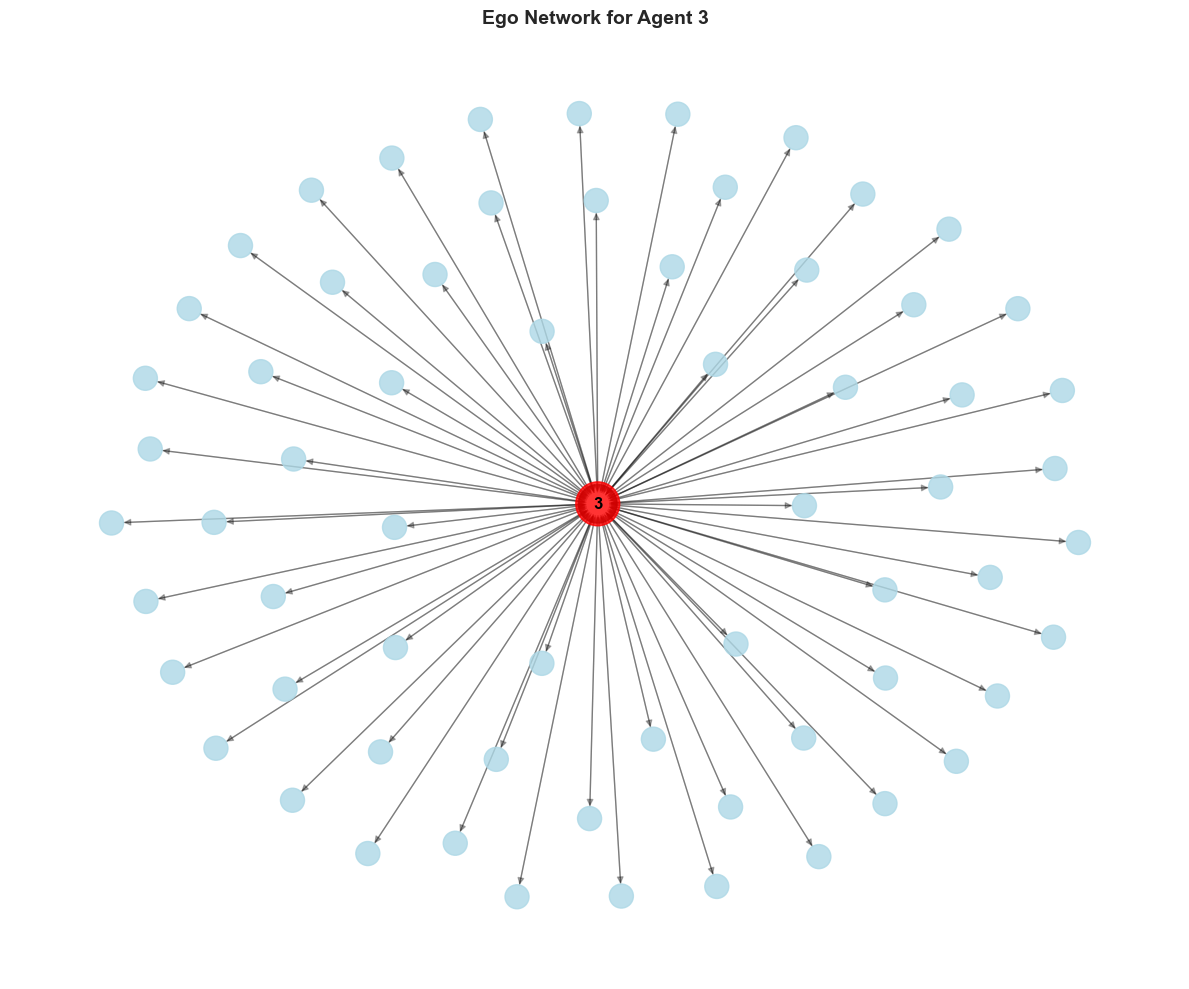
5. Ego Networks
An ego network contains a focal node and all nodes connected to it.
[10]:
# Get ego network for a specific agent
focal_agent = 3 # Change to any agent ID
ego_net = ydh.ego_network(focal_agent)
print(f"Ego Network for Agent {focal_agent}:")
print(f" Nodes: {ego_net.number_of_nodes()}")
print(f" Edges: {ego_net.number_of_edges()}")
print(f" Degree of focal node: {ego_net.degree(focal_agent)}")
Ego Network for Agent 3:
Nodes: 65
Edges: 128
Degree of focal node: 128
Visualizing an Ego Network
[11]:
# Create visualization of ego network
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 10))
# Position nodes using spring layout
pos = nx.spring_layout(ego_net, k=0.5, iterations=50, seed=42)
# Draw nodes
# Focal node in red, others in blue
node_colors = ['red' if node == focal_agent else 'lightblue' for node in ego_net.nodes()]
node_sizes = [1000 if node == focal_agent else 300 for node in ego_net.nodes()]
nx.draw_networkx_nodes(ego_net, pos,
node_color=node_colors,
node_size=node_sizes,
alpha=0.8)
# Draw edges
nx.draw_networkx_edges(ego_net, pos, alpha=0.3, arrows=True, arrowsize=10)
# Draw labels
labels = {node: str(node) if node == focal_agent else '' for node in ego_net.nodes()}
nx.draw_networkx_labels(ego_net, pos, labels, font_size=12, font_weight='bold')
plt.title(f'Ego Network for Agent {focal_agent}', fontsize=14, fontweight='bold')
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
6. Community Detection
Identify communities or clusters within the network.
[12]:
# Use Louvain method for community detection
# Convert to undirected for community detection
undirected_network = social_network.to_undirected()
# Requires python-louvain package
try:
import community as community_louvain
communities = community_louvain.best_partition(undirected_network)
# Count communities
num_communities = len(set(communities.values()))
print(f"Number of Communities Detected: {num_communities}")
# Community sizes
community_sizes = {}
for node, comm_id in communities.items():
community_sizes[comm_id] = community_sizes.get(comm_id, 0) + 1
print("\nCommunity Sizes:")
for comm_id, size in sorted(community_sizes.items(), key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)[:5]:
print(f" Community {comm_id}: {size} nodes")
except ImportError:
print("python-louvain not installed. Install with: pip install python-louvain")
python-louvain not installed. Install with: pip install python-louvain
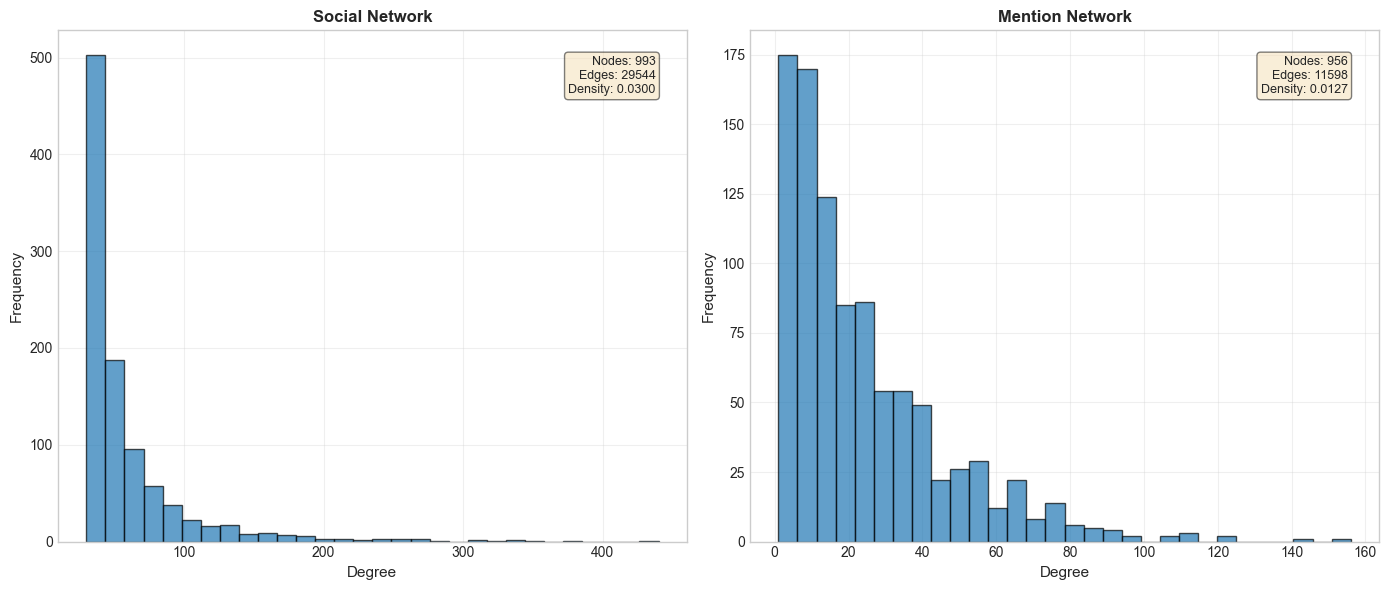
7. Network Comparison
Compare social network with mention network.
[13]:
# Create comparison visualization
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(14, 6))
networks = [social_network, mention_network]
titles = ['Social Network', 'Mention Network']
for ax, net, title in zip(axes, networks, titles):
degrees = [d for n, d in net.degree()]
ax.hist(degrees, bins=30, edgecolor='black', alpha=0.7)
ax.set_xlabel('Degree', fontsize=11)
ax.set_ylabel('Frequency', fontsize=11)
ax.set_title(title, fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
ax.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# Add statistics
ax.text(0.95, 0.95,
f'Nodes: {net.number_of_nodes()}\nEdges: {net.number_of_edges()}\nDensity: {nx.density(net):.4f}',
transform=ax.transAxes,
fontsize=9,
verticalalignment='top',
horizontalalignment='right',
bbox=dict(boxstyle='round', facecolor='wheat', alpha=0.5))
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
Summary
In this tutorial, you learned:
Next Steps
Algorithms Tutorial: Learn about profile similarity, paradox detection, and recommendation metrics
Visualization Tutorial: Create advanced visualizations of simulation data
[ ]:
[ ]: